
AIRS Aerosol Climatology
 |
AIRS 10µm optical depth and altitude of dust aerosols are retrieved simultaneously using a Look-Up-Table (LUT) approach. Altitude is an essential variable for the validation of dust transport models and these retrievals can bring a valuable constrain for assimilation of aerosols with 4D-Var methods. The main advantage of using infrared radiances is the fact that infrared radiation is only sensitive to coarse mode particles, the effect of the accumulation mode and of the width of the distribution being negligible. The effective radius of the dust coarse mode is of particular interest for evaluating the dust radiative forcing.
|
Example result / latest result (if near-real time)
|
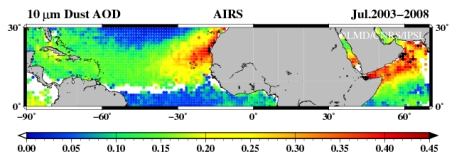 |
| Satellite: | Aqua (NASA) and MetOp (CNES-Eumetsat) |
| Instrument(s): | AIRS and IASI |
| Instrument/algorithm PI: | Sophie Peyridieu, LMD |
| Contact details: | sophie.peyridieu@lmd.polytechnique.fr |
| Parameter(s): | AOD (Infrared, 10 μm) , altitude |
| Aerosol algorithm: | AIRS/IASI Dust |
| Cloud screening: | AIRS/IASI-AMSU BT algorithm |
| Aerosol model: | OPAC MITR |
| Retrieval assumptions: | single dust mode, negligible contribution of other aerosol types, TIGR atmospheres LUT |
| Retrieval limitations: | single dust model |
| Spatial, temporal coverage: | monthly (AIRS: 2003-5-2011, IASI 7/2007-5/2011) and climatology, global |
| Spatial, temporal resolution: | 1° grid, monthly |
| Operations status: | experimental |
| Validation status: | intercomparison with ground-based and other satellite observations (MODIS, CALIOP, PARASOL) |
| Quality control: | simulations use the high spectral resolution fast radiative transfer model 4A/OP – DISORT |
| last algorithm version: | ACP 2010 (19/02/2010) |
| last validation: | 02/2010 |
